class: center, middle, inverse, title-slide # Manipulating data ## JHU Data Science ### www.jtleek.com/advdatasci --- class: inverse, center, middle # dplyr --- ## dplyr verbs * `filter` (and `slice`) : select rows -- * `arrange`: order rows -- * `select` (and `rename`) : order/rename columns -- * `distinct`: find distinct rows -- * `mutate` (and `transmute`): add new variables -- * `summarise`: summarize across a data set -- * `sample_n` and `sample_frac`: sample from a data set -- * `group_by`: Group data by varaible(s) --- ## Gapminder Example ```r install.packages("gapminder") ``` ```r library(dplyr) library(gapminder) str(gapminder) ``` ``` Classes 'tbl_df', 'tbl' and 'data.frame': 1704 obs. of 6 variables: $ country : Factor w/ 142 levels "Afghanistan",..: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ... $ continent: Factor w/ 5 levels "Africa","Americas",..: 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ... $ year : int 1952 1957 1962 1967 1972 1977 1982 1987 1992 1997 ... $ lifeExp : num 28.8 30.3 32 34 36.1 ... $ pop : int 8425333 9240934 10267083 11537966 13079460 14880372 12881816 13867957 16317921 22227415 ... $ gdpPercap: num 779 821 853 836 740 ... ``` ```r gtbl = gapminder ``` --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/gapminder.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center # Gapminder Example .footnote[https://www.ted.com/talks/hans_rosling_shows_the_best_stats_you_ve_ever_seen?language=en] --- class: inverse ## Glimpse - a better `str` ```r glimpse(gtbl) ``` ``` Observations: 1,704 Variables: 6 $ country <fctr> Afghanistan, Afghanistan, Afghanistan, Afghanistan,... $ continent <fctr> Asia, Asia, Asia, Asia, Asia, Asia, Asia, Asia, Asi... $ year <int> 1952, 1957, 1962, 1967, 1972, 1977, 1982, 1987, 1992... $ lifeExp <dbl> 28.801, 30.332, 31.997, 34.020, 36.088, 38.438, 39.8... $ pop <int> 8425333, 9240934, 10267083, 11537966, 13079460, 1488... $ gdpPercap <dbl> 779.4453, 820.8530, 853.1007, 836.1971, 739.9811, 78... ``` --- class: inverse ## Select rows and columns ```r filter(gtbl, lifeExp < 29) ``` ``` # A tibble: 2 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fctr> <fctr> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.801 8425333 779.4453 2 Rwanda Africa 1992 23.599 7290203 737.0686 ``` -- ```r select(gtbl, country, year, pop) ``` ``` # A tibble: 1,704 x 3 country year pop <fctr> <int> <int> 1 Afghanistan 1952 8425333 2 Afghanistan 1957 9240934 3 Afghanistan 1962 10267083 4 Afghanistan 1967 11537966 5 Afghanistan 1972 13079460 6 Afghanistan 1977 14880372 7 Afghanistan 1982 12881816 8 Afghanistan 1987 13867957 9 Afghanistan 1992 16317921 10 Afghanistan 1997 22227415 # ... with 1,694 more rows ``` --- class: inverse ## Order rows ascending and descending ```r arrange(gtbl, pop) %>% head(3) ``` ``` # A tibble: 3 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fctr> <fctr> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 Sao Tome and Principe Africa 1952 46.471 60011 879.5836 2 Sao Tome and Principe Africa 1957 48.945 61325 860.7369 3 Djibouti Africa 1952 34.812 63149 2669.5295 ``` -- ```r arrange(gtbl, desc(pop)) %>% head(3) ``` ``` # A tibble: 3 x 6 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap <fctr> <fctr> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> 1 China Asia 2007 72.961 1318683096 4959.115 2 China Asia 2002 72.028 1280400000 3119.281 3 China Asia 1997 70.426 1230075000 2289.234 ``` --- class: inverse ## Add new columns ```r gtbl = mutate(gtbl, newVar = lifeExp / gdpPercap) select(gtbl, lifeExp,gdpPercap,newVar) %>% head(3) ``` ``` # A tibble: 3 x 3 lifeExp gdpPercap newVar <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> 1 28.801 779.4453 0.03695064 2 30.332 820.8530 0.03695180 3 31.997 853.1007 0.03750671 ``` --- class: inverse ## Distinct: a better `unique` for data sets ```r sub_gtbl = select(gtbl, country, year) distinct(sub_gtbl) ``` ``` # A tibble: 1,704 x 2 country year <fctr> <int> 1 Afghanistan 1952 2 Afghanistan 1957 3 Afghanistan 1962 4 Afghanistan 1967 5 Afghanistan 1972 6 Afghanistan 1977 7 Afghanistan 1982 8 Afghanistan 1987 9 Afghanistan 1992 10 Afghanistan 1997 # ... with 1,694 more rows ``` --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/big_data.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center # Key principle of big data --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/careful.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center # Key principle of big data --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/dogma.png) background-size: 90% background-position: center # Central dogma of statistics --- class: inverse ## Sampling ```r n1000 = sample_n(gtbl, 1000) ``` ```r pct0.5= sample_frac(gtbl, 0.5) dim(pct0.5) ``` ``` [1] 852 7 ``` <font style='font-size:30pt'> Also good with `group_by` for stratified sampling. </font> --- class: inverse, middle, center # Pipes --- class: inverse, middle, center # %>% <font style='font-size:30pt'> Read as "then" </font> <br> <font style='font-size:30pt'> http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/magrittr/index.html </font> --- class: inverse, middle # Piping stuff ```r gtbl %>% head(3) ``` ``` # A tibble: 3 x 7 country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap newVar <fctr> <fctr> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.801 8425333 779.4453 0.03695064 2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.332 9240934 820.8530 0.03695180 3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 31.997 10267083 853.1007 0.03750671 ``` <font style='font-size:30pt'> RStudio does tab completion with column names of a data set. <br> No more "what did I call that variable again?" </font> --- class: inverse, middle, center # Uh...big deal? --- class: inverse, center, middle ## Example <font color="yellow" style='font-size:30pt'> Show me a random sample of size 10 for the data of Asian countries with life expectancy < 65. </font> --- class: inverse ## In base R: ```r # new table gtbl1 = gtbl[gtbl$continent=="Asia",] # reassignment gtbl2 = gtbl1[gtbl1$lifeExp < 65,] # functions in brackets gtbl3 = gtbl2[sample(1:dim(gtbl2)[1],size=10),] gtbl3 ``` --- class: inverse ## With pipes + dplyr ```r gtbl %>% filter(continent == "Asia") %>% filter(lifeExp < 65) %>% sample_n(10) gtbl %>% filter(continent == "Asia", lifeExp < 65) %>% sample_n(10) gtbl %>% filter(continent == "Asia" & lifeExp < 65) %>% sample_n(10) ``` --- class: inverse ## Getting complicated, but readable ```r gtbl %>% filter(year > 1960) %>% group_by(country) %>% sample_n(10) %>% mutate(pop_exp = pop / lifeExp, sampled = TRUE) ``` ``` # A tibble: 1,420 x 9 # Groups: country [142] country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap newVar <fctr> <fctr> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1987 40.822 13867957 852.3959 0.04789089 2 Afghanistan Asia 1982 39.854 12881816 978.0114 0.04075003 3 Afghanistan Asia 1997 41.763 22227415 635.3414 0.06573317 4 Afghanistan Asia 1962 31.997 10267083 853.1007 0.03750671 5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.088 13079460 739.9811 0.04876881 6 Afghanistan Asia 2007 43.828 31889923 974.5803 0.04497115 7 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.438 14880372 786.1134 0.04889626 8 Afghanistan Asia 1992 41.674 16317921 649.3414 0.06417887 9 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.020 11537966 836.1971 0.04068419 10 Afghanistan Asia 2002 42.129 25268405 726.7341 0.05797031 # ... with 1,410 more rows, and 2 more variables: pop_exp <dbl>, # sampled <lgl> ``` --- class: inverse, center, middle ## Example 2 <font color="yellow" style='font-size:30pt'> What is the average life expectancy by continent? </font> --- class: inverse ## With pipes + dplyr ```r gtbl %>% group_by(continent) %>% summarize(aveLife = mean(lifeExp)) ``` ``` # A tibble: 5 x 2 continent aveLife <fctr> <dbl> 1 Africa 48.86533 2 Americas 64.65874 3 Asia 60.06490 4 Europe 71.90369 5 Oceania 74.32621 ``` --- class: inverse ## Multiple Summarizations: just add more ```r gtbl %>% group_by(continent) %>% summarize(aveLife = mean(lifeExp), n = n()) ``` ``` # A tibble: 5 x 3 continent aveLife n <fctr> <dbl> <int> 1 Africa 48.86533 624 2 Americas 64.65874 300 3 Asia 60.06490 396 4 Europe 71.90369 360 5 Oceania 74.32621 24 ``` --- class: inverse # Common Summarization options - mean: mean within groups - sum: sum within groups - sd: standard deviation within groups - max: max within groups - ... ... dplyr functions: - `n()`: number in each group - `first()`: first in group - `last()`: last in group - `nth(n=3)`: nth in group (3rd here) - `tally()` is short-hand for `summarise(n = n())` (see `add_tally`) - `count()` is a short-hand for `group_by() + tally()` (see `add_count`) --- class: inverse, middle, center # dplyr lab <font color="blue" style='font-size:40pt'> https://goo.gl/bryfeH </font> --- class: inverse, middle, center # Merging Data Sets --- class: inverse, middle, center # The worst and most common task --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/joins.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center .footnote[https://www.blubgoo.com/sql-join-overview/] --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/relational.png) background-size: 60% background-position: center .footnote[http://r4ds.had.co.nz/relational-data.html] --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/inner_join.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center # Inner Join<img src="../imgs/manipulating_data/relational.png" style="width:20%"> --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/left_join.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center # Left Join<img src="../imgs/manipulating_data/relational.png" style="width:20%"> --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/full_join.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center # Full Join<img src="../imgs/manipulating_data/relational.png" style="width:20%"> .footnote[http://r4ds.had.co.nz/relational-data.html] --- class: inverse ## Superheroes Example ```r superheroes <- c(" name, alignment, gender, publisher", " Magneto, bad, male, Marvel", " Storm, good, female, Marvel", "Mystique, bad, female, Marvel", " Batman, good, male, DC", " Joker, bad, male, DC", "Catwoman, bad, female, DC", " Hellboy, good, male, Dark Horse Comics") superheroes <- read.csv(text = superheroes, strip.white = TRUE) head(superheroes) ``` ``` name alignment gender publisher 1 Magneto bad male Marvel 2 Storm good female Marvel 3 Mystique bad female Marvel 4 Batman good male DC 5 Joker bad male DC 6 Catwoman bad female DC ``` .footnote[http://stat545.com/bit001_dplyr-cheatsheet.html] --- class: inverse ## Superheroes Example ```r publishers <- c("publisher, yr_founded", " DC, 1934", " Marvel, 1939", " Image, 1992") publishers <- read.csv(text = publishers, strip.white = TRUE) head(publishers) ``` ``` publisher yr_founded 1 DC 1934 2 Marvel 1939 3 Image 1992 ``` .footnote[http://stat545.com/bit001_dplyr-cheatsheet.html] --- ```r ijsp = inner_join(superheroes, publishers) ``` ``` Joining, by = "publisher" ``` ``` Warning: Column `publisher` joining factors with different levels, coercing to character vector ``` 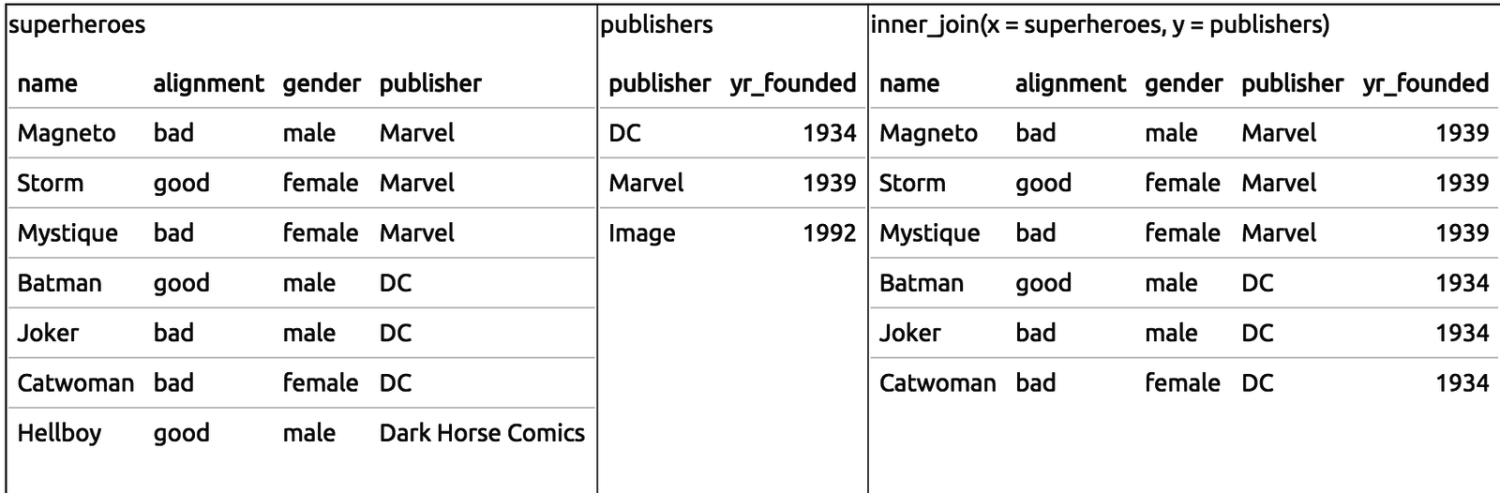 .footnote[http://stat545.com/bit001_dplyr-cheatsheet.html] --- ```r ljsp = left_join(superheroes, publishers) ``` ``` Joining, by = "publisher" ``` ``` Warning: Column `publisher` joining factors with different levels, coercing to character vector ``` 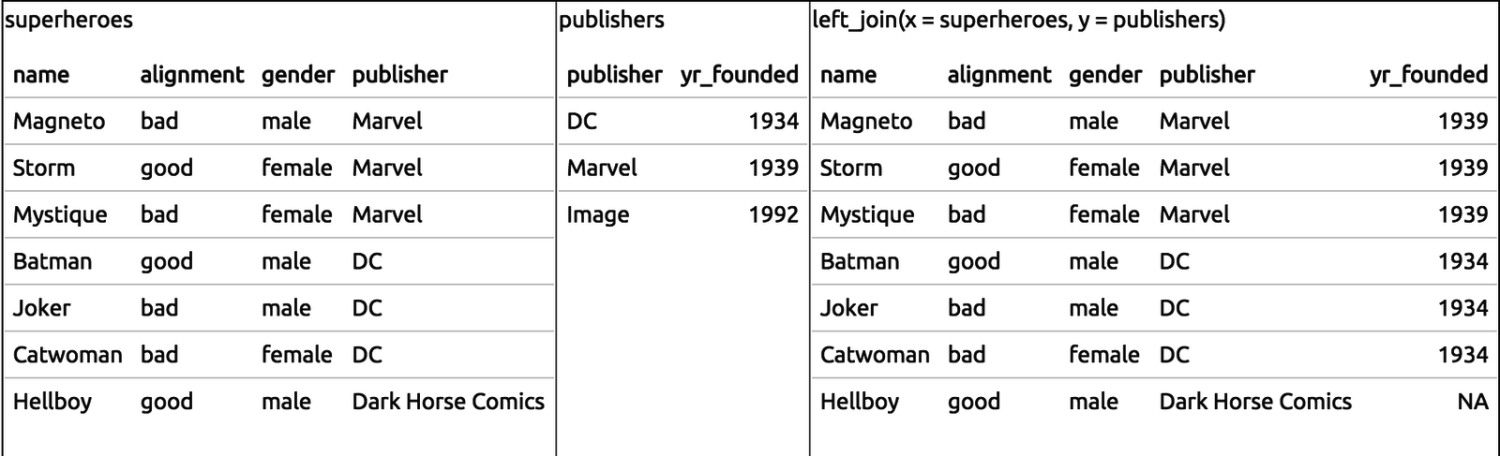 .footnote[http://stat545.com/bit001_dplyr-cheatsheet.html] --- ```r fjsp = left_join(superheroes, publishers) ``` ``` Joining, by = "publisher" ``` ``` Warning: Column `publisher` joining factors with different levels, coercing to character vector ``` 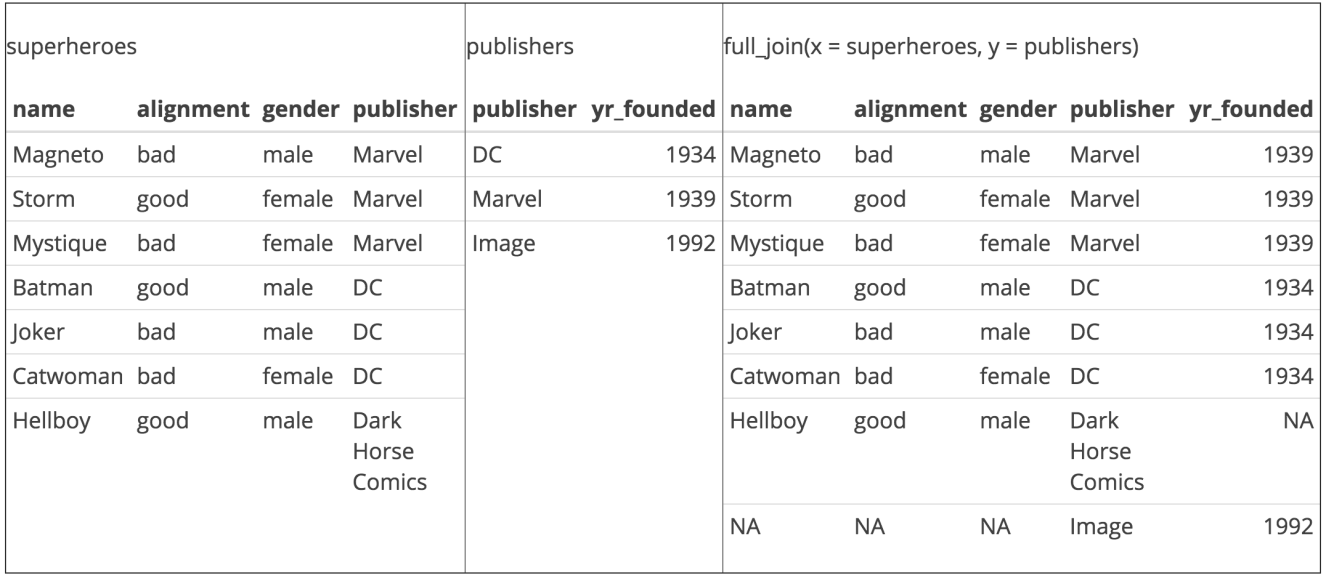 .footnote[http://stat545.com/bit001_dplyr-cheatsheet.html] --- class: inverse, middle, center # Merging lab <font color="blue" style='font-size:40pt'> https://goo.gl/Z3hqyT </font> --- class: inverse, middle, center # dplyr + databases --- class: inverse layout: false ## "flat files" vs. databases <!-- .left-column-equal[Flat files --> .pull-left[Flat files - Formats - .csv, .xlsx, .txt, ... - How used - Usually read into RAM - Good for - Small/medium sized data - Disadvantage - Big data = big computer - Slow reading ] <!-- .right-column-equal[ --> .pull-right[Databases - Formats - sqllite, postgres, mongodb - How used - Data stays on disk - Good for - Big data - Disadvantage - Low interactivity - Potentially slow I/O ] --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/database.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center .footnote[http://r4ds.had.co.nz/relational-data.html] --- class: inverse ## Setup ```r # install.packages("dplyr") # install.packages("babynames") # install.packages("pryr") library(dplyr) library(babynames) library(pryr) ``` --- class: inverse ## Checking out babynames ```r ?babynames View(babynames) ``` ```r str(babynames) ``` ``` Classes 'tbl_df', 'tbl' and 'data.frame': 1858689 obs. of 5 variables: $ year: num 1880 1880 1880 1880 1880 1880 1880 1880 1880 1880 ... $ sex : chr "F" "F" "F" "F" ... $ name: chr "Mary" "Anna" "Emma" "Elizabeth" ... $ n : int 7065 2604 2003 1939 1746 1578 1472 1414 1320 1288 ... $ prop: num 0.0724 0.0267 0.0205 0.0199 0.0179 ... ``` ```r pryr::object_size(babynames) ``` ``` 71.6 MB ``` --- class: inverse ## Getting set up ```r my_db <- src_sqlite("my_db.sqlite3", create = TRUE) babys_sqlite <- copy_to(my_db, babynames, temporary = FALSE, overwrite = TRUE) src_tbls(my_db) ``` ``` [1] "babynames" "sqlite_stat1" ``` ```r tbl(my_db,"babynames") ``` ``` # Source: table<babynames> [?? x 5] # Database: sqlite 3.11.1 # [/Users/johnmuschelli/Dropbox/Teaching/advdatasci/slides/my_db.sqlite3] year sex name n prop <dbl> <chr> <chr> <int> <dbl> 1 1880 F Mary 7065 0.07238433 2 1880 F Anna 2604 0.02667923 3 1880 F Emma 2003 0.02052170 4 1880 F Elizabeth 1939 0.01986599 5 1880 F Minnie 1746 0.01788861 6 1880 F Margaret 1578 0.01616737 7 1880 F Ida 1472 0.01508135 8 1880 F Alice 1414 0.01448711 9 1880 F Bertha 1320 0.01352404 10 1880 F Sarah 1288 0.01319618 # ... with more rows ``` --- class: inverse ## Now you can use dplyr just like before! ```r newtbl = my_db %>% tbl("babynames")%>% filter( name == "Hilary") %>% select(year,n,name, sex) ``` -- `dplyr` waits to access the database. Here it only gets the first 10 rows: ```r newtbl ``` ``` # Source: lazy query [?? x 4] # Database: sqlite 3.11.1 # [/Users/johnmuschelli/Dropbox/Teaching/advdatasci/slides/my_db.sqlite3] year n name sex <dbl> <int> <chr> <chr> 1 1882 7 Hilary M 2 1883 6 Hilary M 3 1887 7 Hilary M 4 1891 8 Hilary M 5 1896 6 Hilary M 6 1897 5 Hilary M 7 1898 5 Hilary M 8 1902 8 Hilary M 9 1904 5 Hilary M 10 1905 6 Hilary M # ... with more rows ``` -- --- class: inverse ## Now you can use dplyr just like before! ```r newtbl = my_db %>% tbl("babynames") %>% filter(name=="Hilary") %>% select(year,n,name, sex) ``` `collect()` asks for the whole result ```r output = newtbl %>% collect() dim(output) ``` ``` [1] 191 4 ``` --- class: inverse ```r library(ggplot2) output %>% filter(year > 1930) %>% ggplot(aes(x = year, y = n, colour = sex)) + geom_line() + ggtitle("Incidence of babies named Hilary") + theme(legend.position = c(0.25, 0.75)) ``` 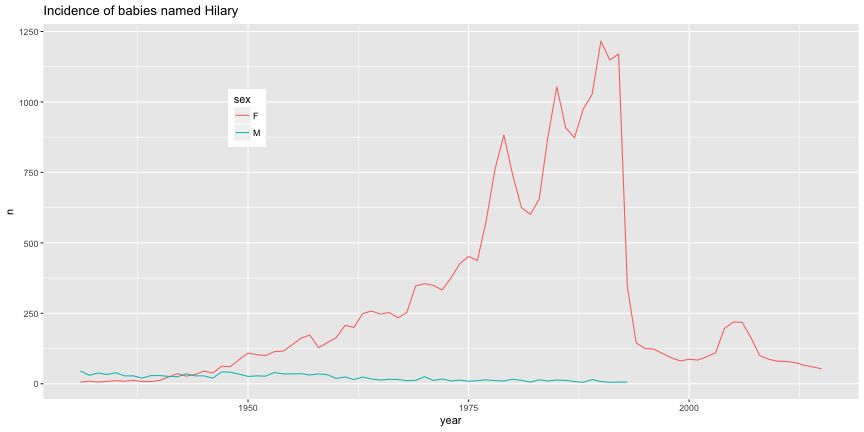<!-- --> --- class: inverse ## Top 100 Baby Names: `data.frame`. ```r popular = babynames %>% group_by(name) %>% summarise(N = sum(n)) %>% arrange(desc(N)) %>% top_n(100) ``` ``` Selecting by N ``` .footnote[http://cpsievert.github.io/slides/intro/#44] --- class: inverse ## Top 100 Baby Names: database ```r popular = my_db %>% tbl("babynames")%>% group_by(name) %>% summarise(N = sum(n)) %>% arrange(desc(N)) %>% top_n(100) ``` ``` Selecting by N ``` This won't work out of the box as `rank` is not supported for this database (so `top_n` is not either) -- ```r popular ``` ``` Error: Window function `rank()` is not supported by this database ``` .footnote[http://cpsievert.github.io/slides/intro/#44] --- class: inverse ## Top 100 Baby Names: database ```r popular = my_db %>% tbl("babynames")%>% group_by(name) %>% summarise(N = sum(n)) %>% arrange(desc(N)) %>% collect() %>% top_n(100) ``` ``` Selecting by N ``` -- ```r popular %>% head(3) ``` ``` # A tibble: 3 x 2 name N <chr> <int> 1 James 5144205 2 John 5117331 3 Robert 4823167 ``` .right[ .footnote[http://cpsievert.github.io/slides/intro/#44] ] --- class: inverse ## Operations in Databases - basic math operators: +, -, *, /, %%, ^ - math functions: abs, acos, acosh, asin, asinh, atan, atan2, atanh, ceiling, cos, cosh, cot, coth, exp, floor, log,log10, round, sign, sin, sinh, sqrt, tan, tanh - logical comparisons: <, <=, !=, >=, >, ==, %in% - boolean operations: &, &&, |, ||, !, xor - basic aggregations: mean, sum, min, max, sd, var .footnote[https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/dplyr/vignettes/databases.html] --- class: inverse ## SQL Translation! ```r suppressPackageStartupMessages({library(dbplyr)}) translate_sql(filter(name=="James")) ``` ``` <SQL> FILTER("name" = 'James') ``` ```r translate_sql(filter(df,name=="James")) ``` ``` <SQL> FILTER("df", "name" = 'James') ``` ```r translate_sql(summarize(group_by(df), mean(x))) ``` ``` <SQL> SUMMARIZE(GROUP_BY("df"), avg("x") OVER ()) ``` --- class: inverse ## SQL Translation with pipes ```r translate_sql({ df %>% group_by(continent) %>% summarize(x = mean(x)) }) ``` ``` Warning: Named arguments ignored for SQL SUMMARIZE ``` ``` <SQL> (SUMMARIZE(GROUP_BY("df", "continent"), avg("x") OVER () AS "x")) ``` --- class: inverse ## Explain details: runs SQL EXPLAIN (query plan) ```r how_female = my_db %>% tbl("babynames") %>% group_by(name) %>% summarize(m = mean(sex == "F")) explain(how_female) ``` ``` <SQL> SELECT `name`, AVG(`sex` = 'F') AS `m` FROM `babynames` GROUP BY `name` ``` ``` ``` ``` <PLAN> addr opcode p1 p2 p3 p4 p5 comment 1 0 Init 0 43 0 00 NA 2 1 SorterOpen 1 2 0 k(1,B) 00 NA 3 2 Integer 0 5 0 00 NA 4 3 Integer 0 4 0 00 NA 5 4 Null 0 8 8 00 NA 6 5 Gosub 7 40 0 00 NA 7 6 OpenRead 0 2 0 3 00 NA 8 7 Rewind 0 13 0 00 NA 9 8 Column 0 2 10 00 NA 10 9 Column 0 1 11 00 NA 11 10 MakeRecord 10 2 12 00 NA 12 11 SorterInsert 1 12 0 00 NA 13 12 Next 0 8 0 01 NA 14 13 Close 0 0 0 00 NA 15 14 OpenPseudo 2 12 2 00 NA 16 15 SorterSort 1 42 0 00 NA 17 16 SorterData 1 12 2 00 NA 18 17 Column 2 0 9 00 NA 19 18 Compare 8 9 1 k(1,B) 00 NA 20 19 Jump 20 24 20 00 NA 21 20 Move 9 8 1 00 NA 22 21 Gosub 6 34 0 00 NA 23 22 IfPos 5 42 0 00 NA 24 23 Gosub 7 40 0 00 NA 25 24 Column 2 1 13 00 NA 26 25 Eq 14 10 13 (BINARY) 62 NA 27 26 AggStep0 0 10 2 avg(1) 01 NA 28 27 Column 2 0 1 00 NA 29 28 Integer 1 4 0 00 NA 30 29 SorterNext 1 16 0 00 NA 31 30 Gosub 6 34 0 00 NA 32 31 Goto 0 42 0 00 NA 33 32 Integer 1 5 0 00 NA 34 33 Return 6 0 0 00 NA 35 34 IfPos 4 36 0 00 NA 36 35 Return 6 0 0 00 NA 37 36 AggFinal 2 1 0 avg(1) 00 NA 38 37 Copy 1 15 1 00 NA 39 38 ResultRow 15 2 0 00 NA 40 39 Return 6 0 0 00 NA 41 40 Null 0 1 3 00 NA 42 41 Return 7 0 0 00 NA 43 42 Halt 0 0 0 00 NA 44 43 Transaction 0 0 180 0 01 NA 45 44 TableLock 0 2 0 babynames 00 NA 46 45 String8 0 14 0 F 00 NA 47 46 Goto 0 1 0 00 NA ``` --- class: inverse, middle, center # Databases lab <font color="blue" style='font-size:40pt'> https://goo.gl/ekBcv1 </font> --- class: inverse, middle, center # When tidy won't do --- background-image: url(../imgs/manipulating_data/nmeth.png) background-size: 100% background-position: center .footnote[http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/v12/n2/full/nmeth.3252.html] --- class: inverse, middle, center # tidygenomics ```r install.packages("tidygenomics") ```